More information
Main author
Melanie Kreutner
Co-Authors
Christoph Lauterwasser
Type of media
Publication type
Lecture
Publication year
2018
Publisher
27. EVU Conference, Dubrovnik
Citation
-
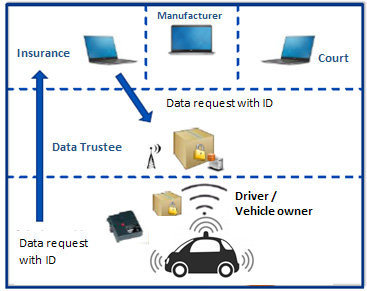
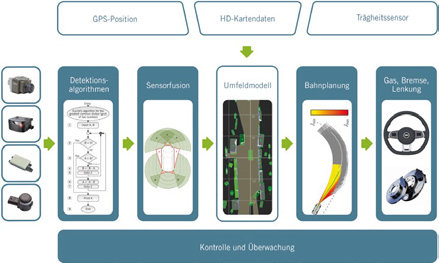
The article gives a current overview of the experience of AZT with the complexity and limitations of storing accident and event data and with technical access. It is apparent that a variety of event data is already stored in modern vehicles, but at the same time, a universal standard for all models, brands or manufacturers has not been established. In crash tests, there were good correlations with respect to the CDR data measured by external measuring technology and the CDR data logged by the vehicle – provided that the limitations in data generation in the vehicle were recognized and taken into account. With highly automated vehicles in mind, in the revision of the German Road Traffic Act (§ 63a StVG), the Federal Republic of Germany has made it mandatory to provide standardized and regulated data storage which is restricted to information for determining the driving mode. Regulation of access to this data and the specific configuration of a data model are yet to be provided. Allianz supports the model of an independent data trustee, allowing authorized persons easy, tamper-proof, fair and non-discriminatory access to the relevant data elements.In the work group AHEAD, with the support of AZT and additional cooperation partners, a data model that is intended to allow proper investigation of accidents and events involving highly automated vehicles in the future is being developed. Relevant data elements from the driving data, the environment and object recognition, the driver activity and the crash are to be defined, and data and formats are to be standardized. In crash tests, the designed data model is validated and evaluated. The aim is for this data model to ultimately be able to be used as a basis in the standardization work for the homologation of highly automated vehicles (Level 3 and above).
(EVU-members can download the full article)